Page 91 - Remedial Andrology
P. 91
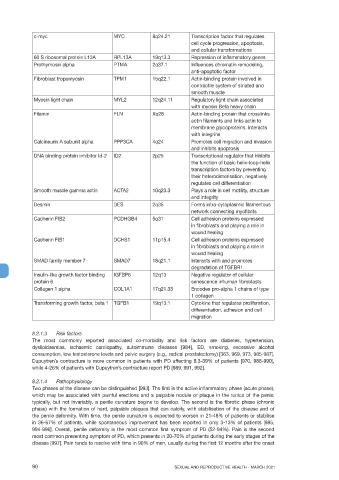
c-myc MYC 8q24.21 Transcription factor that regulates
cell cycle progression, apoptosis,
and cellular transformations
60 S ribosomal protein L13A RPL13A 19q13.3 Repression of inflammatory genes
Prothymosin alpha PTMA 2q37.1 Influences chromatin remodeling,
anti-apoptotic factor
Fibroblast tropomyosin TPM1 15q22.1 Actin-binding protein involved in
contractile system of striated and
smooth muscle
Myosin light chain MYL2 12q24.11 Regulatory light chain associated
with myosin Beta heavy chain
Filamin FLN Xq28 Actin-binding protein that crosslinks
actin filaments and links actin to
membrane glycoproteins. Interacts
with integrins
Calcineurin A subunit alpha PPP3CA 4q24 Promotes cell migration and invasion
and inhibits apoptosis
DNA binding protein inhibitor Id-2 ID2 2p25 Transcriptional regulator that inhibits
the function of basic helix-loop-helix
transcription factors by preventing
their heterodimerisation, negatively
regulates cell differentiation
Smooth muscle gamma actin ACTA2 10q23.3 Plays a role in cell motility, structure
and integrity
Desmin DES 2q35 Forms intra-cytoplasmic filamentous
network connecting myofibrils
Cadherin FIB2 PCDHGB4 5q31 Cell adhesion proteins expressed
in fibroblasts and playing a role in
wound healing
Cadherin FIB1 DCHS1 11p15.4 Cell adhesion proteins expressed
in fibroblasts and playing a role in
wound healing
SMAD family member 7 SMAD7 18q21.1 Interacts with and promotes
degradation of TGFBR1
Insulin-like growth factor binding IGFBP6 12q13 Negative regulator of cellular
protein 6 senescence inhuman fibroblasts
Collagen 1 alpha COL1A1 17q21.33 Encodes pro-alpha 1 chains of type
1 collagen
Transforming growth factor, beta 1 TGFB1 19q13.1 Cytokine that regulates proliferation,
differentiation, adhesion and cell
migration
8.2.1.3 Risk factors
The most commonly reported associated co-morbidity and risk factors are diabetes, hypertension,
dyslipidaemias, ischaemic cardiopathy, autoimmune diseases [984], ED, smoking, excessive alcohol
consumption, low testosterone levels and pelvic surgery (e.g., radical prostatectomy) [363, 969, 973, 985-987].
Dupuytren’s contracture is more common in patients with PD affecting 8.3-39% of patients [970, 988-990],
while 4-26% of patients with Dupuytren’s contracture report PD [989, 991, 992].
8.2.1.4 Pathophysiology
Two phases of the disease can be distinguished [993]. The first is the active inflammatory phase (acute phase),
which may be associated with painful erections and a palpable nodule or plaque in the tunica of the penis;
typically, but not invariably, a penile curvature begins to develop. The second is the fibrotic phase (chronic
phase) with the formation of hard, palpable plaques that can calcify, with stabilisation of the disease and of
the penile deformity. With time, the penile curvature is expected to worsen in 21-48% of patients or stabilise
in 36-67% of patients, while spontaneous improvement has been reported in only 3-13% of patients [985,
994-996]. Overall, penile deformity is the most common first symptom of PD (52-94%). Pain is the second
most common presenting symptom of PD, which presents in 20-70% of patients during the early stages of the
disease [997]. Pain tends to resolve with time in 90% of men, usually during the first 12 months after the onset
90 SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH - MARCH 2021