Page 44 - Remedial Andrology
P. 44
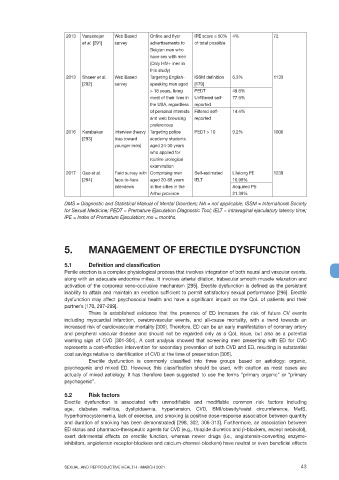
2013 Vansintejan Web Based Online and flyer IPE score < 50% 4% 72
et al. [291] survey advertisements to of total possible
Belgian men who
have sex with men
(Only HIV+ men in
this study)
2013 Shaeer et al. Web Based Targeting English- ISSM definition 6.3% 1133
[292] survey speaking men aged [179]
> 18 years, living PEDT 49.6%
most of their lives in Unfiltered self- 77.6%
the USA, regardless reported
of personal interests Filtered self- 14.4%
and web browsing reported
preferences
2016 Karabakan Interview (heavy Targeting police PEDT > 10 9.2% 1000
[293] bias toward academy students
younger men) aged 24-30 years
who applied for
routine urological
examination
2017 Gao et al. Field survey with Comprising men Self-estimated Lifelong PE 1239
[294] face-to-face aged 20-68 years IELT 10.98%
interviews in five cities in the Acquired PE
Anhui province 21.39%
DMS = Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; NA = not applicable; ISSM = International Society
for Sexual Medicine; PEDT = Premature Ejaculation Diagnostic Tool; IELT = intravaginal ejaculatory latency time;
IPE = Index of Premature Ejaculation; mo = months.
5. MANAGEMENT OF ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION
5.1 Definition and classification
Penile erection is a complex physiological process that involves integration of both neural and vascular events,
along with an adequate endocrine milieu. It involves arterial dilation, trabecular smooth muscle relaxation and
activation of the corporeal veno-occlusive mechanism [295]. Erectile dysfunction is defined as the persistent
inability to attain and maintain an erection sufficient to permit satisfactory sexual performance [296]. Erectile
dysfunction may affect psychosocial health and have a significant impact on the QoL of patients and their
partner’s [170, 297-299].
There is established evidence that the presence of ED increases the risk of future CV events
including myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular events, and all-cause mortality, with a trend towards an
increased risk of cardiovascular mortality [300]. Therefore, ED can be an early manifestation of coronary artery
and peripheral vascular disease and should not be regarded only as a QoL issue, but also as a potential
warning sign of CVD [301-304]. A cost analysis showed that screening men presenting with ED for CVD
represents a cost-effective intervention for secondary prevention of both CVD and ED, resulting in substantial
cost savings relative to identification of CVD at the time of presentation [305].
Erectile dysfunction is commonly classified into three groups based on aetiology: organic,
psychogenic and mixed ED. However, this classification should be used, with caution as most cases are
actually of mixed aetiology. It has therefore been suggested to use the terms “primary organic” or “primary
psychogenic”.
5.2 Risk factors
Erectile dysfunction is associated with unmodifiable and modifiable common risk factors including
age, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidaemia, hypertension, CVD, BMI/obesity/waist circumference, MetS,
hyperhomocysteinemia, lack of exercise, and smoking (a positive dose-response association between quantity
and duration of smoking has been demonstrated) [298, 302, 306-313]. Furthermore, an association between
ED status and pharmaco-therapeutic agents for CVD (e.g., thiazide diuretics and β-blockers, except nebivolol),
exert detrimental effects on erectile function, whereas newer drugs (i.e., angiotensin-converting enzyme-
inhibitors, angiotensin-receptor-blockers and calcium-channel-blockers) have neutral or even beneficial effects
SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH - MARCH 2021 43