Page 46 - Remedial Andrology
P. 46
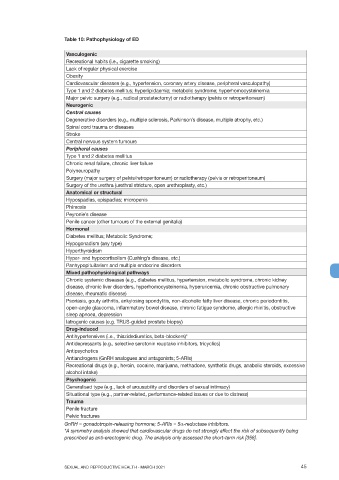
Table 10: Pathophysiology of ED
Vasculogenic
Recreational habits (i.e., cigarette smoking)
Lack of regular physical exercise
Obesity
Cardiovascular diseases (e.g., hypertension, coronary artery disease, peripheral vasculopathy)
Type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus; hyperlipidaemia; metabolic syndrome; hyperhomocysteinemia
Major pelvic surgery (e.g., radical prostatectomy) or radiotherapy (pelvis or retroperitoneum)
Neurogenic
Central causes
Degenerative disorders (e.g., multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, multiple atrophy, etc.)
Spinal cord trauma or diseases
Stroke
Central nervous system tumours
Peripheral causes
Type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus
Chronic renal failure, chronic liver failure
Polyneuropathy
Surgery (major surgery of pelvis/retroperitoneum) or radiotherapy (pelvis or retroperitoneum)
Surgery of the urethra (urethral stricture, open urethroplasty, etc.)
Anatomical or structural
Hypospadias, epispadias; micropenis
Phimosis
Peyronie’s disease
Penile cancer (other tumours of the external genitalia)
Hormonal
Diabetes mellitus; Metabolic Syndrome;
Hypogonadism (any type)
Hyperthyroidism
Hyper- and hypocortisolism (Cushing’s disease, etc.)
Panhypopituitarism and multiple endocrine disorders
Mixed pathophysiological pathways
Chronic systemic diseases (e.g., diabetes mellitus, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, chronic kidney
disease, chronic liver disorders, hyperhomocysteinemia, hyperuricemia, chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease, rheumatic disease)
Psoriasis, gouty arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, chronic periodontitis,
open-angle glaucoma, inflammatory bowel disease, chronic fatigue syndrome, allergic rhinitis, obstructive
sleep apnoea, depression
Iatrogenic causes (e.g. TRUS-guided prostate biopsy)
Drug-induced
Antihypertensives (i.e., thiazidediuretics, beta-blockers)*
Antidepressants (e.g., selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, tricyclics)
Antipsychotics
Antiandrogens (GnRH analogues and antagonists; 5-ARIs)
Recreational drugs (e.g., heroin, cocaine, marijuana, methadone, synthetic drugs, anabolic steroids, excessive
alcohol intake)
Psychogenic
Generalised type (e.g., lack of arousability and disorders of sexual intimacy)
Situational type (e.g., partner-related, performance-related issues or due to distress)
Trauma
Penile fracture
Pelvic fractures
GnRH = gonadotropin-releasing hormone; 5-ARIs = 5α-reductase inhibitors.
*A symmetry analysis showed that cardiovascular drugs do not strongly affect the risk of subsequently being
prescribed as anti-erectogenic drug. The analysis only assessed the short-term risk [356].
SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH - MARCH 2021 45