Page 130 - Remedial Andrology
P. 130
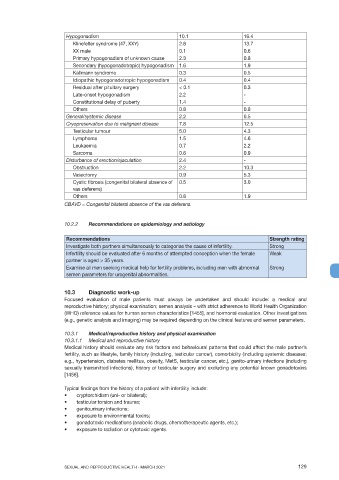
Hypogonadism 10.1 16.4
Klinefelter syndrome (47, XXY) 2.6 13.7
XX male 0.1 0.6
Primary hypogonadism of unknown cause 2.3 0.8
Secondary (hypogonadotropic) hypogonadism 1.6 1.9
Kallmann syndrome 0.3 0.5
Idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism 0.4 0.4
Residual after pituitary surgery < 0.1 0.3
Late-onset hypogonadism 2.2 -
Constitutional delay of puberty 1.4 -
Others 0.8 0.8
General/systemic disease 2.2 0.5
Cryopreservation due to malignant disease 7.8 12.5
Testicular tumour 5.0 4.3
Lymphoma 1.5 4.6
Leukaemia 0.7 2.2
Sarcoma 0.6 0.9
Disturbance of erection/ejaculation 2.4 -
Obstruction 2.2 10.3
Vasectomy 0.9 5.3
Cystic fibrosis (congenital bilateral absence of 0.5 3.0
vas deferens)
Others 0.8 1.9
CBAVD = Congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens.
10.2.2 Recommendations on epidemiology and aetiology
Recommendations Strength rating
Investigate both partners simultaneously to categorise the cause of infertility. Strong
Infertility should be evaluated after 6 months of attempted conception when the female Weak
partner is aged > 35 years.
Examine all men seeking medical help for fertility problems, including men with abnormal Strong
semen parameters for urogenital abnormalities.
10.3 Diagnostic work-up
Focused evaluation of male patients must always be undertaken and should include: a medical and
reproductive history; physical examination; semen analysis – with strict adherence to World Health Organization
(WHO) reference values for human semen characteristics [1455], and hormonal evaluation. Other investigations
(e.g., genetic analysis and imaging) may be required depending on the clinical features and semen parameters.
10.3.1 Medical/reproductive history and physical examination
10.3.1.1 Medical and reproductive history
Medical history should evaluate any risk factors and behavioural patterns that could affect the male partner’s
fertility, such as lifestyle, family history (including, testicular cancer), comorbidity (including systemic diseases;
e.g., hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity, MetS, testicular cancer, etc.), genito-urinary infections (including
sexually transmitted infections), history of testicular surgery and excluding any potential known gonadotoxins
[1456].
Typical findings from the history of a patient with infertility include:
• cryptorchidism (uni- or bilateral);
• testicular torsion and trauma;
• genitourinary infections;
• exposure to environmental toxins;
• gonadotoxic medications (anabolic drugs, chemotherapeutic agents, etc.);
• exposure to radiation or cytotoxic agents.
SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH - MARCH 2021 129