Page 85 - Remedial Andrology
P. 85
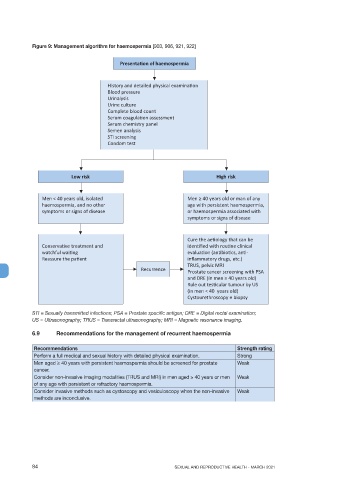
Figure 9: Management algorithm for haemospermia [903, 906, 921, 922]
Presenta on of haemospermia
History and detailed physical examina on
Blood pressure
Urinalysis
Urine culture
Complete blood count
Serum coagula on assessment
Serum chemistry panel
Semen analysis
STI screening
Condom test
Low risk High risk
Men < 40 years old, isolated Men ≥ 40 years old or man of any
haemospermia, and no other age with persistent haemospermia,
symptoms or signs of disease or haemospermia associated with
symptoms or signs of disease
Cure the ae ology that can be
Conserva ve treatment and iden fied with rou ne clinical
watchful wai ng evalua on (an bio cs, an -
Reassure the pa ent inflammatory drugs, etc.)
TRUS, pelvic MRI
Recurrence Prostate cancer screening with PSA
and DRE (in men ≥ 40 years old)
Rule out tes cular tumour by US
(in men < 40 years old)
Cystourethroscopy ± biopsy
STI = Sexually transmitted infections; PSA = Prostate specific antigen; DRE = Digital rectal examination;
US = Ultrasonography; TRUS = Transrectal ultrasonography; MRI = Magnetic resonance imaging.
6.9 Recommendations for the management of recurrent haemospermia
Recommendations Strength rating
Perform a full medical and sexual history with detailed physical examination. Strong
Men aged > 40 years with persistent haemospermia should be screened for prostate Weak
cancer.
Consider non-invasive imaging modalities (TRUS and MRI) in men aged ≥ 40 years or men Weak
of any age with persistent or refractory haemospermia.
Consider invasive methods such as cystoscopy and vesiculoscopy when the non-invasive Weak
methods are inconclusive.
84 SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH - MARCH 2021