Page 103 - Remedial Andrology
P. 103
All the autologous grafts have the inconvenience of possible graft harvesting complications. Dermal grafts are
commonly associated with veno-occlusive ED (20%) due to lack of adaptability, so they have not been used
in contemporary series [1141, 1142, 1145-1155]. Vein grafts have the theoretical advantage of endothelial-
to-endothelial contact when grafted to underlying cavernosal tissue. The saphenous vein has been the most
commonly used vein graft [1156-1171]. For some extensive albuginea defects, more than one incision may be
needed. Tunica albuginea grafts have perfect histological properties but have some limitations: the size that can
be harvested, the risk of weakening penile support and making future procedures (penile prosthesis implantation)
more complicated [1172-1174]. Tunica vaginalis is easy to harvest and has little tendency to contract due to its
low metabolic requirements, although better results can be obtained if a vascular flap is used [1175-1179]. Under
the pretext that by placing the submucosal layer on the corpus cavernosum the graft feeds on it and adheres
more quickly, the buccal mucosal graft has recently been used with good short-term results [1180-1186].
Cadaveric dura mater is no longer used due to concerns about the possibility of infection [1187, 1188].
©
Cadaveric pericardium (Tutoplast ) offers good results by coupling excellent tensile strength and
multidirectional elasticity/expansion by 30% [1077, 1140, 1151, 1189, 1190]. Cadaveric or autologous fascia
lata or temporalis fascia offers biological stability and mechanical resistance [1191-1193].
Xenografts have become more popular in recent years. Small intestinal submucosa (SIS), a type I collagen-
based xenogenic graft derived from the submucosal layer of the porcine small intestine, has been shown to
promote tissue-specific regeneration and angiogenesis, and supports host cell migration, differentiation and
growth of endothelial cells, resulting in tissue structurally and functionally similar to the original [1194-1203]. As
mentioned above, pericardium (bovine, in this case) has good traction resistance and adaptability, and good
©
host tolerance [1171, 1204-1207]. Grafting by collagen fleece (TachoSil ) in PD has some major advantages
such as decreased operating times, easy application and an additional haemostatic effect [1208-1213].
®
It is generally recommended that synthetic grafts, including polyester (Dacron ) and polytetrafluoroethylene
(Gore-Tex ) are avoided, due to increased risks of infection, secondary graft inflammation causing tissue
®
fibrosis, graft contractures, and possibility of allergic reactions [1116, 1214-1217].
Some authors recommend post-operative penile rehabilitation to improve surgical outcomes. Some studies have
described using VED and PTT to prevent penile length loss of up to 1.5 cm [1218]. Daily nocturnal administration
of PDE5I enhances nocturnal erections, encourages perfusion of the graft, and may minimise post-operative ED
[1219]. Massages and stretching of the penis have also been recommended once wound healing is complete.
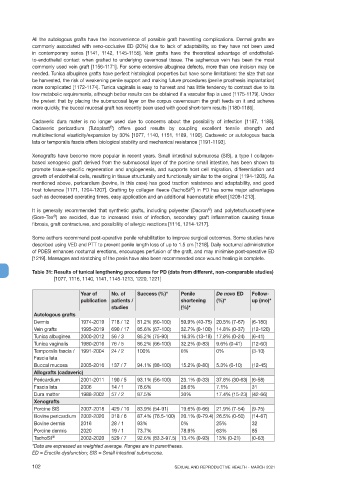
Table 31: Results of tunical lengthening procedures for PD (data from different, non-comparable studies)
[1077, 1116, 1140, 1141, 1145-1213, 1220, 1221]
Year of No. of Success (%)* Penile De novo ED Follow-
publication patients / shortening (%)* up (mo)*
studies (%)*
Autologous grafts
Dermis 1974-2019 718 / 12 81.2% (60-100) 59.9% (40-75) 20.5% (7-67) (6-180)
Vein grafts 1995-2019 690 / 17 85.6% (67-100) 32.7% (0-100) 14.8% (0-37) (12-120)
Tunica albuginea 2000-2012 56 / 3 85.2% (75-90) 16.3% (13-18) 17.8% (0-24) (6-41)
Tunica vaginalis 1980-2016 76 / 5 86.2% (66-100) 32.2% (0-83) 9.6% (0-41) (12-60)
Temporalis fascia / 1991-2004 24 / 2 100% 0% 0% (3-10)
Fascia lata
Buccal mucosa 2005-2016 137 / 7 94.1% (88-100) 15.2% (0-80) 5.3% (0-10) (12-45)
Allografts (cadaveric)
Pericardium 2001-2011 190 / 5 93.1% (56-100) 23.1% (0-33) 37.8% (30-63) (6-58)
Fascia lata 2006 14 / 1 78.6% 28.6% 7.1% 31
Dura matter 1988-2002 57 / 2 87.5% 30% 17.4% (15-23) (42-66)
Xenografts
Porcine SIS 2007-2018 429 / 10 83.9% (54-91) 19.6% (0-66) 21.9% (7-54) (9-75)
Bovine pericardium 2002-2020 318 / 6 87.4% (76.5-100) 20.1% (0-79.4) 26.5% (0-50) (14-67)
Bovine dermis 2016 28 / 1 93% 0% 25% 32
Porcine dermis 2020 19 / 1 73.7% 78.9% 63% 85
TachoSil ® 2002-2020 529 / 7 92.6% (83.3-97.5) 13.4% (0-93) 13% (0-21) (0-63)
*Data are expressed as weighted average. Ranges are in parentheses.
ED = Erectile dysfunction; SIS = Small intestinal submucosa.
102 SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH - MARCH 2021